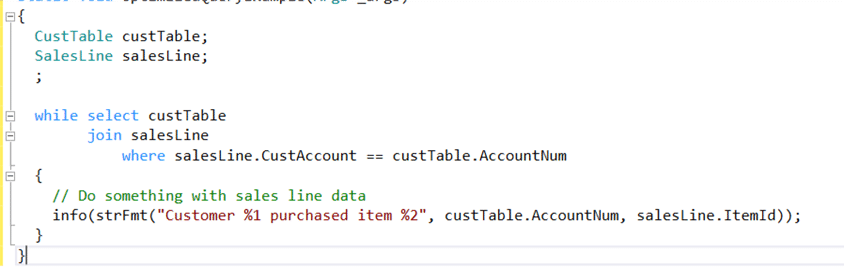
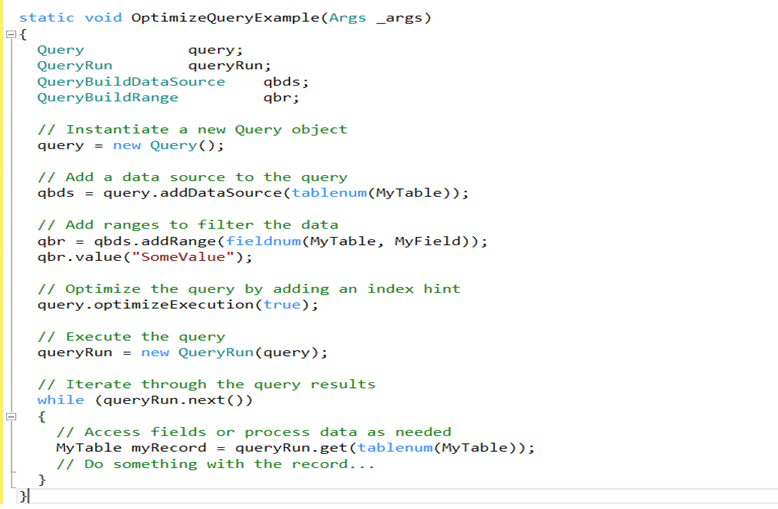
Performance issues are a common concern for Microsoft Dynamics 365 solutions. They often arise when performance considerations are not adequately addressed during system implementation, upgrades, and modifications.
To ensure your Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations environment operates at its best, it is important to conduct regular audits, develop optimization plans, and identify and resolve performance bottlenecks.
SQL query optimization plays a key role in Dynamics 365 performance optimization. It enhances database query performance by refining the query’s execution plan while preserving its result.
This blog will cover the concept of query optimization in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations, explore common challenges, and provide techniques and best practices for effective SQL query optimization.
What is query optimization?
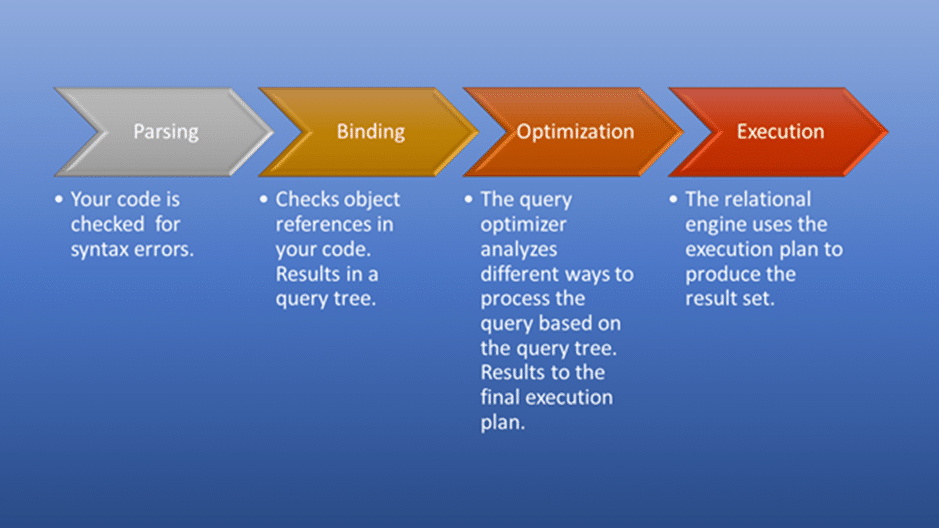
Query optimization is the process of choosing the most efficient means of executing SQL queries. The goal is to reduce the time and resources required to retrieve data from a database while maintaining the accuracy and integrity of the results.
SQL is a non-procedural language, so the optimizer is free to merge, reorganize, and process in any order. The database optimizes each SQL statement based on statistics collected about the accessed data.
Query optimization in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations (F&O) refers to the process of enhancing the efficiency and speed of SQL queries executed within the system. This process involves various techniques and best practices to improve data retrieval performance, reduce resource consumption, and ensure the system runs smoothly. Effective query optimization can significantly impact the overall performance of Dynamics 365 F&O, leading to faster response times and a more efficient use of system resources.
Common challenges in Query Optimization
Optimizing queries can be complex due to various factors that affect performance. Here are some of the common issues in Dynamics 365 F&O query optimization:
- Complex data structures: Intricate relationships between tables can complicate query design and optimization, leading to inefficient data retrieval.
- Large data volumes: Handling extensive datasets can result in slow query performance and high resource consumption.
- Suboptimal indexing: Ineffective or missing indexes can degrade query performance, slowing data retrieval and increasing database load.
- Poor query design: Inefficient query writing, such as using SELECT * or unnecessary joins, can lead to excessive data retrieval and slow response times.
- High concurrency: Concurrent access can cause locking and contention issues, impacting overall query performance and system responsiveness.
How to optimize queries in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations?
Optimizing SQL query performance in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations (D365 F&O) is essential for maintaining efficient and responsive systems. Here are some Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O query optimization techniques:
- Understand the context: When optimizing queries in D365 F&O, ensure that you focus on queries within the D365 F&O environment to avoid optimizing the wrong elements.
- Add missing indexes: Improve query performance by adding appropriate indexes. Create indexes on columns that are frequently used in WHERE clauses to speed up query performance.
- Avoid multiple OR conditions: Simplify queries to reduce complexity and improve execution time. Use UNION or other alternatives to avoid multiple OR conditions, which can slow down queries.
- Use wildcards judiciously: Use wildcards only when necessary to prevent slow searches. Place wildcards at the end of search patterns rather than the beginning to improve search efficiency.
- Minimize JOINs: Reduce the number of JOINs in queries to decrease complexity and execution time.
- Avoid SELECT DISTINCT: Use more specific query conditions to achieve unique results without SELECT DISTINCT.
- Specify SELECT fields: Specify only the necessary fields in SELECT statements instead of using SELECT * to reduce data retrieval time.
- Use TOP to sample query results: The TOP clause limits the number of rows returned, which can speed up query execution.
- Run queries during off-peak hours: Schedule heavy queries during off-peak hours to minimize impact on system performance.
- Minimize query hints: Avoid excessive use of query hints, as they can override the query optimizer’s decisions and degrade performance.
- Reduce large write operations: Break down large write operations into smaller batches to avoid locking and improve performance.